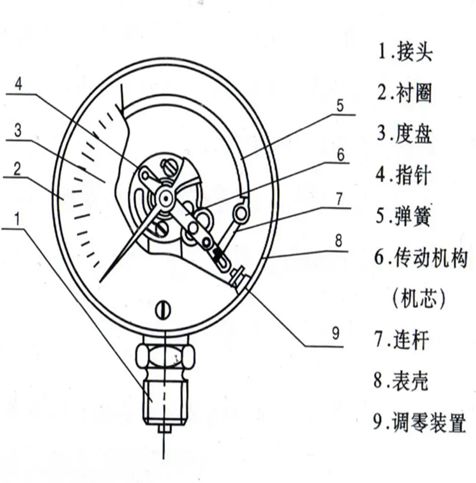
詳細(xì)介紹
全場景覆蓋!壓力表檢測周期與安全使用手冊
#全場景壓力表檢測 #行業(yè)專用壓力表檢測周期 #壓力表安全使用 #壓力表日常巡檢維護(hù)
Full-scenario coverage! Pressure gauge inspection cycle and safety manual
Pressure gauges are widely used in various industries such as chemical, power, metallurgy, municipal administration, and medicine, serving as the "eyes" that ensure smooth production processes and prevent safety accidents. Pressure gauges in different industries and scenarios exhibit significant differences in their operating environments, pressure tolerances, and medium characteristics, leading to varying inspection cycles and usage requirements. Many companies, due to a lack of thorough understanding of the scenario-specific requirements for inspection cycles, face potential safety hazards during the use of pressure gauges. This article will comprehensively cover various application scenarios, provide a detailed analysis of the inspection cycle standards and key points for safe use of pressure gauges, and offer a comprehensive guide for companies to standardize the management of pressure gauges.
The chemical industry is one of the fields where pressure gauges are used under the most stringent conditions. The media in this industry are often corrosive, toxic, and flammable, and the operating pressure and temperature fluctuate greatly, imposing extremely strict requirements on the inspection cycle of pressure gauges. For pressure gauges that come into contact with strong acids, strong alkalis, and toxic media, such as those on sulfuric acid storage tanks, hydrochloric acid transfer pipelines, and toxic gas reactors, the inspection cycle must be set to once every six months due to the rapid erosion of the elastic elements and seals of the pressure gauges by the media, leading to issues such as indication deviation and leakage. Special verification of the pressure gauge's sealing and corrosion resistance is required during each inspection. For pressure gauges used in the storage of inert gases (such as nitrogen and argon) in the chemical industry, if the operating conditions are stable, the inspection cycle can be appropriately extended to once a year, but routine inspections need to be strengthened, and any abnormalities found must be immediately inspected.
Pressure gauges in the power industry are primarily utilized in equipment such as boilers, steam turbines, and steam pipelines, and are categorized as supporting instruments for special equipment. Their inspection cycles must strictly adhere to relevant regulations for special equipment. Pressure gauges on the boiler's upper drum and main steam pipeline directly monitor high-temperature and high-pressure steam pressure, serving as core instruments for ensuring the safe operation of the boiler. Their inspection cycle must be once every six months. Pressure gauges in the lubricating oil system and cooling water system of the steam turbine, which operate under relatively mild conditions, can have an inspection cycle set at once a year. Furthermore, during major maintenance of the power unit, regardless of whether it is within the inspection cycle, comprehensive inspection and calibration of pressure gauges are required to ensure the accuracy and reliability of the instruments after the unit is restarted.
Pressure gauges in the municipal industry are primarily utilized in scenarios such as tap water supply systems, gas transmission pipelines, and wastewater treatment equipment. Their inspection cycles need to be set in consideration of public safety and operational characteristics. For pressure gauges in tap water supply pipelines, the medium is room temperature tap water, and the operating conditions are stable, thus the inspection cycle can be set to once a year. However, for pressure gauges used in secondary water supply pressurization equipment, due to significant pressure fluctuations during equipment operation, the inspection cycle needs to be shortened to once every nine months. For pressure gauges in gas transmission pipelines, the medium is flammable and explosive gas, posing a high safety risk, thus the inspection cycle needs to be once every six months. During inspection, it is crucial to verify the pressure resistance and sealing performance of the pressure gauge to prevent gas leakage. For pressure gauges in wastewater treatment plants, the medium contains a large amount of corrosive impurities, thus the inspection cycle also needs to be once every six months. During inspection, special cleaning and calibration of the pressure gauge's probe and interface are required.
Pressure gauges in the pharmaceutical industry are directly related to the quality of drug production and medication safety, and their testing cycles are closely linked to cleanliness requirements. Pressure gauges used in sterile drug production equipment (such as fermentation tanks and sterilization cabinets) not only need to comply with pressure testing standards but also meet GMP certification requirements. The testing cycle is set at once every six months, and during the testing process, the cleanliness of the pressure gauge must be ensured to avoid contaminating the drug production environment. For ordinary auxiliary equipment in the pharmaceutical industry (such as purified water storage tanks), the testing cycle can be set at once a year. In addition, pressure gauge testing records in the pharmaceutical industry must be kept complete to ensure the traceability of the drug production process.
Regardless of the scenario, the safe use of pressure gauges cannot be separated from standardized daily inspections and maintenance. Enterprises need to establish a pressure gauge ledger, detailing information such as the model, installation location, inspection cycle, and inspection results of pressure gauges. Daily inspections should focus on the pointer status, dial cleanliness, and interface tightness of pressure gauges. If issues such as pointer stagnation, abnormal values, or leaks are found, the pressure gauge must be immediately suspended from use and sent for inspection. At the same time, pressure gauges that have been idle for more than six months and those that have undergone maintenance must pass inspection before being put back into use. Only by strictly enforcing the inspection cycle and strengthening daily management in combination with the characteristics of the scenario can the monitoring role of pressure gauges be fully utilized to ensure production safety and quality stability in various industries.
#Full-scenario pressure gauge testing #Industry-specific pressure gauge testing cycle #Safe use of pressure gauge #Routine inspection and maintenance of pressure gauge